- Helping people save money and eat better.
- In Food Talk project, we would like to create a device with an application that help people to reduce food waste, which is essential to save their budget. Furthermore, it is equally an food advisor for each family to help them have better food and better nutrition for every member in family.
Our Vision
Food waste issues - it is time to react!
The issues of global food waste has received much attention in recent years from developed countries. According to FAO in 2011, approximately one third of all food produced for human consumption – around 1.3 billion tons per years – is lost or wasted globally, which cost almost $750 billion. In EU, nearly 100 million tons of food are wasted each year (estimate for 2012). Wasting food is not only a humanitarian concern and economic issue but it also depletes the environment of limited natural resources.
What is food waste?
In a report of FAO published in 2013, food waste is defined as "intentional discards of edible items, mainly by retailers and consumers, and is due to the behavior of businesses and individuals". Food waste often occurs in developed countries because consumers fail to plan their shopping, over purchase, or over-react to "best-before-dates," while quality and aesthetic standards lead retailers to reject large amounts of perfectly edible food. In addition, excessive nutrition is considered as a form of food waste (Barilla, 2012). People in developed countries have a tendency to consume more food which led to the excessive calories requirement. Thus, a larger excess growth was recorded in obesity rates (OECD, 2014), which leds to several pathologies.
Food waste is different from food loss
Food loss is the unintended reduction in food available for human consumption that results from inefficiencies in supply chains: poor infrastructure and logistics, lack of technology, insufficient skills, knowledge and management capacity. It mainly occurs at production- postharvest and processing stages, for example when food goes unharvested or is damaged during processing, storage and transport and disposed of (FAO, 2013).
Food loss usually occur in developing countries as a result of financial and structural limitations in harvesting techniques and storage and transport infrastructure, combined with climatic conditions favorable to food spoilage.
Households is main source of food waste
Consumer behavior is a main driver of food going to waste. Almost one third of food wastage is from consumption level in developed countries. In Europe, 50% of food waste is generated in private households (FUSION, 2015). According to a study of WRAP in UK, about 2/3 of household waste is due to food spoilage from not being used in time, 1/3 is caused by people cooking or serving too much.
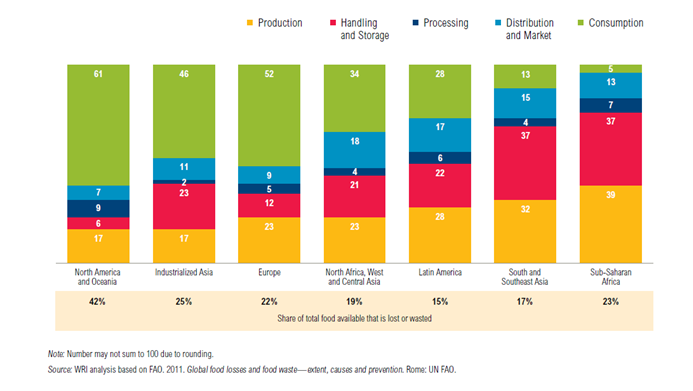
Food Lost or Wasted By Region and Stage in Value Chain, 2009 (Percent of kcal lost and wasted)
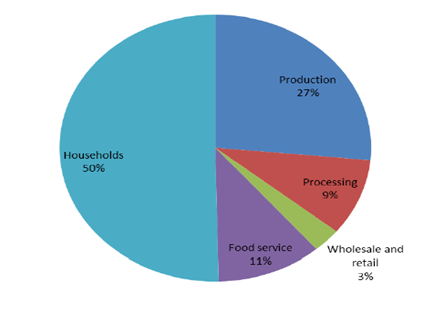
Source of food waste in Europe (Survey of FUSION, 2015)
Wasting food is wasting money and natural resources
According to numerous reports, food waste cost much money. In USA, The cost estimate for the average family of four is $1,365 to $2,275 each year. Average UK household spend £470 for wasting food. Additionally, UK household with children spend more than 32% of waste food cost. By reducing food waste amount, a household in EU would save almost 600 € per year . (EU, 2014)
Furthermore, food waste consumes much energy. A report from Mc Kinsey Global Institute in 2011 reveals that household waste are responsible for eight times the energy waste of post-harvest losses on average due to the energy used along the supply chain and in food preparation.
Wasting food reduces overall supply and drives up food prices. During the last ten years, food costs have increased to 42% .
This makes food less affordable for those who are poor and malnourished in other parts of the world. According to World Bank in 2010, rising food prices pushes 44 million people into poverty . The worldwide food insecurity is at an all time high, with nearly 1 billion people hungry .
Producing food that is squandered also wastes important finite resources such as oil, freshwater, soil fertility, land, various ecosystem services as well as undocumented human labor:
- Food wastage's carbon footprint is estimated at 3.3 billion tones of CO2 equivalent of greenhouse gases emission released into the atmosphere per year.
- The total volume of water used annually to produce food that is lost or wasted (250km3) is equivalent to three times the volume of Lake Geneva.
- Similarly, 1.4 billion hectares of land - 28 % of the world's agricultural area - is used each year to produce uneaten food.
- Food waste consumes more than 300 million barrels of oil per year (4% of total U.S. oil consumption)
Consumers having a great power in reducing food waste
As a consumer, you have a great power in reducing the total amount of food waste by taking measures on all levels of your daily lives: Shopping, storing and cooking habits need to be revised. Furthermore, you can influence production and retail patterns regarding food waste. Surveys (EU, 2014) reveal that consumers are willing to purchase heterogeneous ("misshapen") products if the taste is not concerned. Thus, you could pressure the farmers and wholesalers via the retailers not to sort out "misshapen" fruits and vegetables and force retailers to loosen their aesthetic standards.
Food Talk is consumers's friend against food waste
Changing your habit is not easy although you are aware that food waste is a big issue to tackle. With the aim to help consumers achieve the goal of reducing food waste and saving their budget, Food Talk has been developed with functions as below:
- Measuring the right amounts of food based on your needs
- Advice for food preservation
- Reminding the expiration date of your food
- Planning for your shopping
- Proposing simple and healthy recipes
Our team believes that Food Talk by far will become an efficient and necessary tool for each household in developed countries in the movement against food waste.
References
- Barilla Center. 2012. Food waste: causes, impacts and proposals. Italy: Barilla center for food & nutrition.
- Dobbs .R et al. 2011. Resource Revolution: Meeting the World's Energy, Materials, Food and Water Needs. Mc Kinsey Global Institute.
- European Commission. 2014. Food waste and its impacts. European Week for Waste Reduction. Available online at http://www.ewwr.eu.
- FAO. 2013. Food wastage footprint - Impacts on natural resources. FAO.
- FUSIONS. 2015. WP1: Food waste statistic in Europe and how to collect food waste data in the future.
- Gunders, D .2012. Wasted: How America Is Losing Up to 40 Percent of Its Food from Farm to Fork to Landfill. Natural Resources Defense Council.
- Lipinski, B. et al. 2013. Reducing Food Loss and Waste. Working Paper, Installment 2 of Creating a Sustainable Food Future. Washington, DC: World Resources Institute. Available online at http://www.worldresourcesreport.org.
- OECD. 2014. Obesity and the economic of prevention: fit not fat. OECD.
- WRAP. 2015. Estimates of Food and Packaging Waste in the UK Grocery Retail and Hospitality Supply Chains. Available online at http://www.wrap.org.uk.
Prototype
Currently, we are working on our prototype, you can view our presentation below:
Project Idea
Do you know that every year, each person in France throws away about 30 kg of food, and 7kg of the food is still-packaged food products. It costs around 100 euro/person/year, therefore the cost of food waste for a family of 4 people is 400 euros.The total cost for food waste is 12 to 20 billion euros/year.
In the other hand, regarding to a research of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in 2014, overweight and obesity rates in France are among the lowest in Europe, but have been increasing steadily. One in 8 adults is obese in France, and 40% are overweight (including obese).
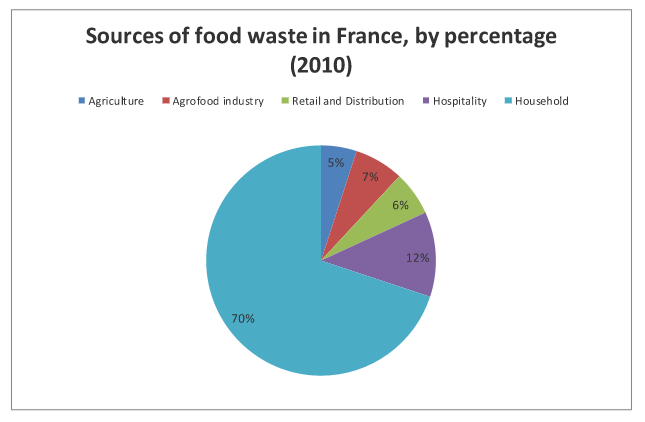
Sources of food waste in France, by percentage (Adapted from Etude Bio Intelligence Service : Preparatory Study on Food Waste across EU 27, 2010)
Do you think two things below is concerned? We can say yes! When you buy more than you need and eat more than your body can absorb, you waste your money because you will throw the products when it is near the expiration date, or you try to eat more than you can, which is worse for your health.
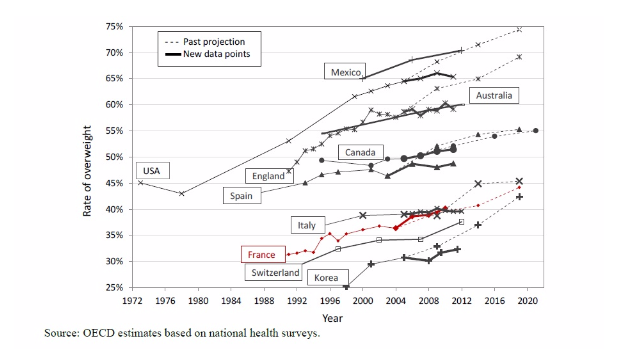
Trends in the prevalence of overweight (including obesity) in adults, projections and recent estimates, selected OECD countries
By introducing our project, we want to make an application that help people to control their weight, reduce food waste in their fridge and also save their money.